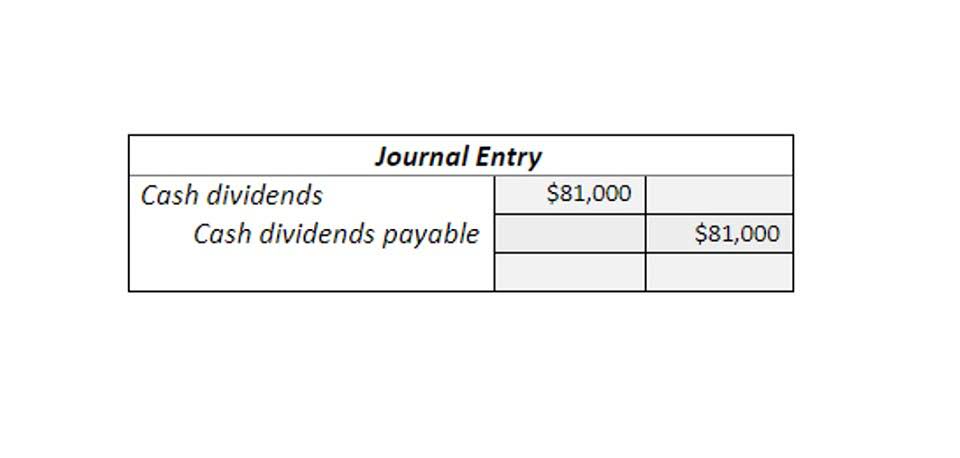
Preferred stock prices are generally also consistent like bond prices and may not offer the potential for growth that most common stock does. However, in the event a company goes bankrupt, preferred stockholders receive payments before common stockholders. Any company bondholders, however, are paid before preferred stockholders. The second step is when the company pays dividends to its shareholders. Assuming it pays dividends in the form of cash, the company must credit its cash account, while also eliminating the balance in the dividends payable account created before. For instance, when the company in the above example pays its shareholders dividends of $10,000, it must use the following accounting treatment to record the transaction.
What is Dividend Policy, and What Are the Different Types of Dividend Policy?

We may earn a commission when you click on a link or make a purchase through the links on our site. All of our content is based on objective analysis, and the opinions are our own. The ex-dividend date is the date after which the traded share will not pay a dividend to its new owner. After this date, the next payment will be made to the original owner. Smaller ratios are less taxing on a company and reducing them has diminishing returns, so they are more likely to remain stable and sustainable.
How Often Are Dividends Distributed to Shareholders?
Let us say the stock price drops from $32 to $27; if that happens, the yield will jump to 6.4%. Many countries also offer preferential tax treatment to dividends, treating them as tax-free income. Dividend payouts may also help provide insight into a company’s intrinsic value.
Chase Security Center
The specifics depend on the type of account that dividend-paying stocks are held in, among other things. Additionally, dividend-paying companies can be seen as stable companies, while growth companies, where value comes from stock price appreciation, may be riskier. If your investment risk tolerance is low, investing in dividend-paying companies may be worthwhile.
All stock dividends require an accounting journal entry for the company issuing the dividend. This entry transfers the value of the issued stock from the retained earnings account to the paid-in capital account. In most cases, a company will pay dividends to its shareholders on a quarterly basis. A company’s board of directors decides how much and how often dividends are paid based on how much money the company makes and what its goals are. A well-laid out financial model will typically have an assumptions section where any return of capital decisions are contained.
The rest of your accounts are set up to provide predictable, long-term growth. But this is the account where you can “scratch an itch.” That might be participating in a type of investing you find interesting, challenging, or stimulating. If your year-end tax liability from your extra income will be more than a few hundred dollars, you can be hit with a large tax bill when you file your return. https://www.bookstime.com/ Even worse, the IRS imposes penalties and interest on nonpayment or underpayment of income tax due. If you want to be really accurate, have an accountant or tax preparer analyze your income for the year and let you know how much you should be allocating for tax payments. Before we get into that, make sure you check the financial integrity of any institution that’s paying high interest rates.
- The easiest way to buy dividend stocks is by opening a brokerage account.
- As you can see in the screenshot, GE declared a dividend per common share of $0.84 in 2017, $0.93 in 2016, and $0.92 in 2015.
- Instead, you swoop in and buy them right before the dividend is paid out.
- Complacency with interest yields costs you money in the form of lost income.
- However, they allow companies more flexibility in how they pay their shareholders.
- Dividends paid by funds are different from dividends paid by companies.
NerdWallet does not and cannot guarantee the accuracy or applicability of any information in regard to your individual circumstances. Examples are hypothetical, and we encourage you to seek personalized advice from qualified professionals regarding specific investment issues. Our estimates are based on past market performance, and past performance is not a guarantee of future performance. In a way, dividends may seem or feel like free money, but in another sense, they’re more like a reward for shareholders for owning a portion of a company. First, creditors are paid from the company’s assets, and then the remaining amount is paid to the equity holders. For property dividends, the company has to assess market value and record the dividend on the fair value.
- It’s a way to build additional wealth even on money earmarked for other purposes.
- Growth stocks, however, often collapse during recessions because they tend to be leveraged when these months occur.
- If you own 100 shares of a company that is trading at $1 a share and paying a dividend of 25%, you would be paid $25.
- A steady track record of paying dividends makes stocks more attractive to investors.
The cheaper “cost-on-yield” makes this a better long-term investment strategy. If a company earns $2 per share in a given quarter and pays a dividend of $1 per share, its payout ratio is said to be 50%. How a stock dividend affects the balance sheet is a bit more involved than cash dividends, although it only involves shareholder equity. When dividends type of account a stock dividend is declared, the amount to be debited is calculated by multiplying the current stock price by shares outstanding by the dividend percentage. Some investors prefer companies that pay dividends because they provide a source of regular income. Additionally, dividend payments can signal that a company is doing well financially.